
In contrast, a patient with moderate to severe hydronephrosis, or with evidence of a urinary tract infection may require a urologic consultation and potentially advanced imaging for interventional planning (eg how large and how proximal is the stone). Patients without infection and no significant obstruction are very likely to pass their stone on their own and are less likely to need advanced imaging unless you are concerned for alternative dangerous abdominal pathology. A patient who you are fairly certain has a kidney stone, and exhibits none or mild hydronephrosis, maybe able to go home once pain controlled and tolerating PO with a normal urinalysis and creatinine. Common pitfalls on ultrasound include misidentifying the renal vessels or medullary pyramids for hydronephrosis.Īlthough a patient with renal colic may exhibit a range of hydronephrosis on a bedside ultrasound, it is still very helpful information to guide your next steps. In addition, there were no significant differences in “high-risk diagnoses with complications, serious adverse events, pain scores, return emergency department visits, or hospitalizations” between initiating with ultrasound versus CT. Initiating kidney imaging with ultrasound was “associated with lower cumulative radiation exposure than initial CT”. Lastly, renal calyces merge to form a renal pelvis which normally appear as collapsed and hyperechoic.Īlthough computer tomography (CT) may also be used as an imaging tool in detecting hydronephrosis and nephrolithiasis, ultrasound has been found to be effective. Important to note that in a normal kidney these pyramids are non-communicating, existing as discrete hypoechoic wedges separated from one another.
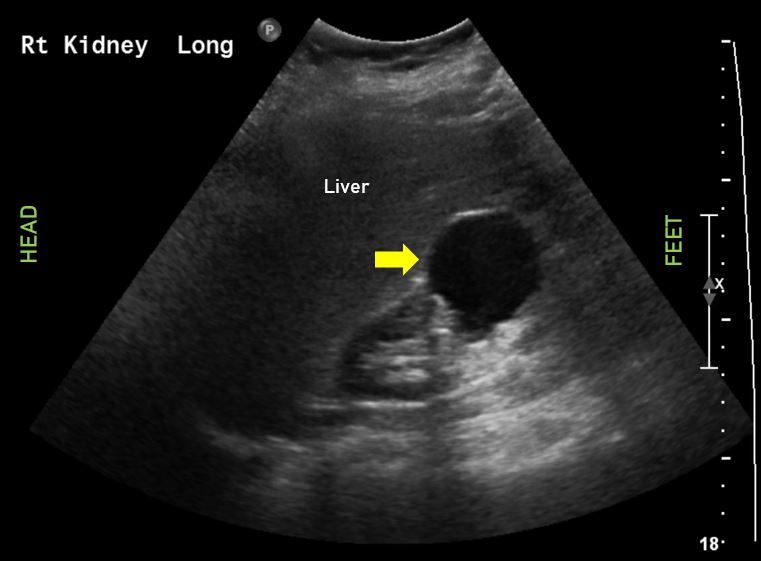
The kidney’s medullary pyramids will appear as dark, hypoechoic wedges on ultrasound. Each kidney’s cortex will usually be 1cm thick and on ultrasound will appear like a liver in terms of echogenicity. Apply color doppler to differentiate between the collecting system, which will not exhibit color flow, and the renal vasculature.Ī normal kidney will be surrounded by a capsule, which appears as a bright white, hyperechoic line on ultrasound. You should scan through the entire kidney slowly on both sides in both the coronal and the transverse planes. Keep in mind that the probe will need to be rotated slightly obliquely, to minimize rib shadow. Meanwhile, on the patient’s left, the probe will be in the posterior axillary line between the 8th to 10th rib space. On the patient’s right side, the probe should be placed in the midaxillary line between the 9th- 11th rib. Discussion:Ī curvilinear or phased array transducer are the best options for a renal ultrasound given their capability for high penetration. Renal ultrasound can be important in determining diagnosis, management, and next steps in the evaluation of a patient with flank or abdominal pain, hematuria, concern for stone and more. While the differential is broad, when one sees this listed as the chief complaint, you may as well bring the ultrasound machine in with you when you go to assess the patient.

Flank pain is a very common presenting complaint for visits in the emergency department (ED), accounting for over two million annual ED visits.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
